Transfer Tours
- From Florence to Venice or Milano with stop in bologna at “FICO Eataly World”
- From Florence to Rome with stop in San Gimignano & Siena
- From Florence to Rome with stop in Perugia & Assisi
- From Florence to Rome via Chianti
- From Florence to Rome with stop in Orvieto
- From Florence to Rome with stop in Pienza & Montepulciano
- From Florence to Rome with Outlets stop
- From Florence to Venice with stop in Padova
- From Florence to Venice with stop in Bologna
- From Florence to Milano with stop in Bologna
- Tours in Tuscany Rent a Car With Driver Service
- From Florence to Milano with stop at Maranello (Ferrari museum)
- From Florence to Rapallo, Santa Margherita Ligure, Portofino with stop in Pisa
- Tours in Florence Car Service
- From Florence to Rapallo, Santa Margherita Ligure, Portofino with stop in 5 Terre
- Customized Transfer Tour
From Florence to Venice with stop in Padova
Your driver will pick you up at your hotel/apartment in FLORENCE
and he'll drive you to VENICE with a stop in PADUA.
Padua, Italy, (Italian: Padova IPA: ['padova], Latin: Patavium, Venetian: Padoa) is a city in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of Padova province and the economic and communications hub of the province. Padua's population is 211,985 (2004). The city is sometimes included, with Venice (Italian Venezia), in the Padua-Venice Metropolitan Area, population 1,600,000.
Padua stands on the Bacchiglione River, and Brenta river (which once passed inside the city) still touches northern districts, 40 km west of Venice and 29km southeast of Vicenza. Its agricultural setting is the Pianura Veneta, the "Venetian plain," To the city's south west lies the Euganaean Hills, praised by Lucan and Martial, Petrarch, Ugo Foscolo, and Shelley.
The city is picturesque, with a dense network of arcaded streets opening into large communal piazze, and many bridges crossing the various branches of the Bacchiglione, which once surrounded the ancient walls like a moat.
Padua is the setting for most of the action in Shakespeare's The Taming of the Shrew.
Main sights
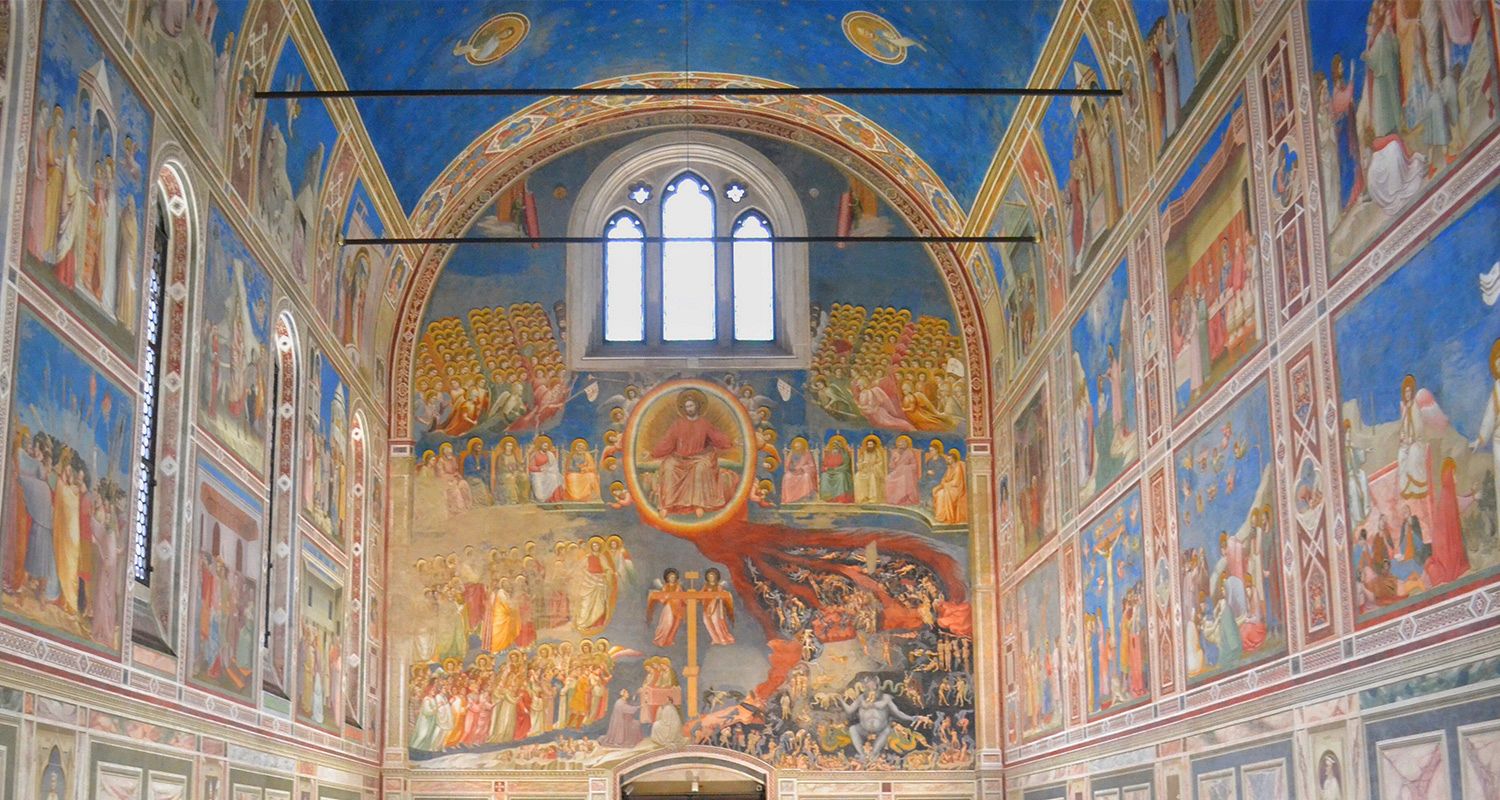
The Scrovegni Chapel (Italian: Cappella degli Scrovegni) is Padua's most famous sight. It houses a remarkable cycle of frescoes completed in 1305 by Giotto. It was Commissioned by Enrico degli Scrovegni, a wealthy banker, as a private chapel once attached to his family's palazzo. It is also called the "Arena Chapel" because it stands on the site of a Roman-era arena. The fresco cycle details the life of the Virgin Mary and has been acknowledged by many to be one of the most important fresco cycles in the world. Entrance to the chapel is an elaborate ordeal, as it involves spending 15 minutes prior to entrance in a climate-controlled, airlocked vault, used to stabilize the temperature between the outside world and the inside of the chapel. This is to improve preservation. Book ahead if planning a visit.
The Palazzo della Ragione, with its great hall on the upper floor, is reputed to have the largest roof unsupported by columns in Europe; the hall is nearly rectangular, its length 81.5 m, its breadth 27 m, and its height 24 m; the walls are covered with allegorical frescoes; the building stands upon arches, and the upper storey is surrounded by an open loggia, not unlike that which surrounds the basilica of Vicenza. The Palazzo was begun in 1172 and finished in 1219. In 1306 Fra Giovanni, an Augustinian friar, covered the whole with one roof. Originally there were three roofs, spanning the three chambers into which the hall was at first divided; the internal partition walls remained till the fire of 1420, when the Venetian architects who undertook the restoration removed them, throwing all three spaces into one and forming the present great hall, the Salone. The new space was refrescoed by Nicolo' Miretto and Stefano da Ferrara, working from 1425 to 1440. Beneath the great hall, there is a centuries-old market.
In the Piazza dei Signori is the beautiful loggia called the Gran Guardia, (1493 - 1526), and close by is the Palazzo del Capitanio, the residence of the Venetian governors, with its great door, the work of Giovanni Maria Falconetto, the Veronese architect-sculptor who introduced Renaissance architecture to Padua and who completed the door in 1532. Falconetto was the architect of Alvise Cornaro's garden loggia, (Loggia Cornaro), the first fully Renaissance building in Padua. Nearby, the Cathedral, remodelled in 1552 after a design of Michelangelo. It contains works by Nicolò Semitecolo, Francesco Bassano and Giorgio Schiavone. The nearby Baptistry, consecrated in 1281, houses the most important frescoes cycle by Giusto de' Menabuoi.
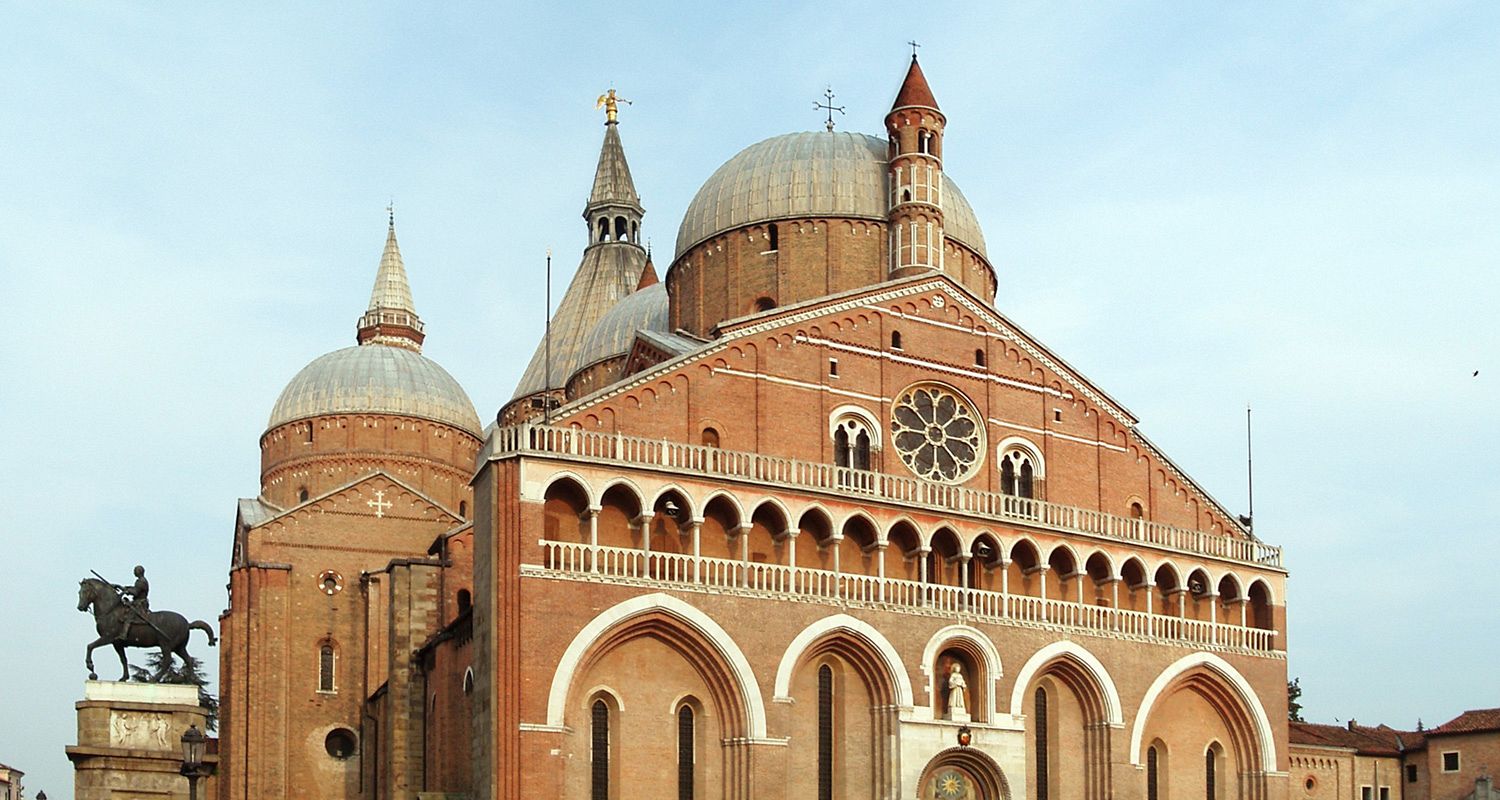
The most famous of the Paduan churches is the Basilica di Sant'Antonio da Padova, locally simply known as "Il Santo". The bones of the saint rest in a chapel richly ornamented with carved marbles, the work of various artists, among them of Sansovino and Falconetto. The basilica was begun about the year 1230 and completed in the following century. Tradition says that the building was designed by Nicola Pisano. It is covered by seven cupolas, two of them pyramidal. There are also four beautiful cloisters to visit. Sant'Antonio is treated as Vatican territory.
Donatello's magnificent equestrian statue of the Venetian general Gattamelata (Erasmo da Narni) can be found on the piazza in front of the Basilica di Sant'Antonio da Padova. It was cast in 1453, and was the first full-size equestrian bronze cast since antiquity. It was inspired by the Marcus Aurelius equestrian sculpture at the Capitoline Hill in Rome.
Not far from the Gattamelata statue are the St. George Oratory (13th century), with frescoes by Altichiero, and the Scuola di S. Antonio (16th century), with frescoes by Tiziano (Titian).
One of the best known symbols of Padua is the Prato della Valle, a 90,000 m² elliptical square. This is believed to be the biggest in Europe, after Red Square in Moscow. In the centre is a wide garden surrounded by a ditch, which is lined by 78 statues portraying famous citizens.
The abbey and the basilica of Santa Giustina. In the 15th century, it became one of the most important monasteries in the area, until it was suppressed by Napoleon in 1810. In 1919 it was reopened. The tombs of several saints are housed in the interior, including those of Justine, St. Prosdocimus, St. Maximus, St. Urius, St. Felicita, St. Julianus, as well as relics of the Apostle St. Matthias and the Evangelist St. Luke. This is home to some art, including the Martyrdom of St. Justine by Paolo Veronese. The complex was founded in the 5th century on the tomb of the namesake saint, Justine of Padua.
The Church of the Eremitani is an Augustinian church of the 13th century, containing the tombs of Jacopo (1324) and Ubertinello (1345) da Carrara, lords of Padua, and for the chapel of SS James and Christopher, formerly illustrated by Mantegna's frescoes. This was largely destroyed by the Allies in World War II, because it was next to the Nazi headquarters. The old monastery of the church now houses the municipal art gallery.
Santa Sofia is most likely Padova's most ancient church. The crypt was begun in the late 10th century by Venetian craftsmen. It has a basilica plan with Romanesque-Gothic interior and Byzantine elements. The apse was built in the 12th century. The edifice appears to be tilting slightly due to the soft terrain.
The church of San Gaetano (1574-1586) was designed by Vincenzo Scamozzi, on an unusual octagonal plan. The interior, decorated with polychrome marbles, houses a precious Madonna and Child by Andrea Briosco, in Nanto stone.
At the centre of the historical city, the buildings of Palazzo del Bò, the centre of the University.
The City Hall, called Palazzo Moroni, the wall of which is covered by the names of the Paduan deads in the different wars of Italy and which is attached to Palazzo della Ragione.
The Caffé Pedrocchi, built in 1831 by architect Giuseppe Jappelli in neoclassical style with Egyptian influence. This is a little jewel of history and art for a café open for almost two centuries. It hosts the Risorgimento museum, and the near building of the Pedrocchino ("little Pedrocchi") in neogothic style.
The city centre is surrounded by the 11km-long city walls, built during the early sixteenth century, by architects that included Michele Sanmicheli. There are only a few ruins left, together with two gates, of the smaller and inner thirteenth-century walls. There is also a castle, the Castello. Its main tower was transformed between 1767 and 1777 into an astronomical observatory known as Specola. However the other buildings were used as prisons during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. They are now being restored.